Most electrical circuits have multiple components in them. We also know that these components have resistance, affecting the flow of current.
Let's find out how the resistance in different circuits varies!
First, let's remind ourselves of some key terms - current and resistance.
In electrical circuits, the current is the rate of flow of electrical charge.
Current is measured in amps, and we can use ammeters to measure it in a circuit.

Every component in a circuit has a resistance. The resistance of a component is a measure of how difficult it is for the current to flow through it.
A high resistance means a low current. A low resistance means a high current.
Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω)
Let's start by considering series circuits, where all the components are in a continuous loop.

The current in this circuit has to pass through all of the components (in this case, four resistors).
We say that the total resistance in this circuit is the sum of all of the individual resistances.
RTotal = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4 + ...
If the resistors each had a resistance of 5 Ω
RTotal = 5 Ω + 5 Ω + 5 Ω + 5 Ω
RTotal = 20 Ω
In series circuits, the more components you add, the more resistance the circuit has. This means that the circuit has a lower current.
Example

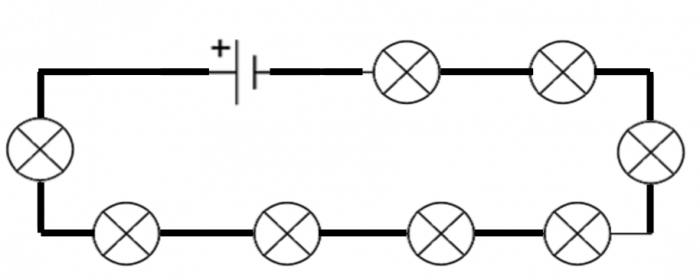
This circuit has eight bulbs. The bulbs are identical.
The total resistance of the circuit is 96 Ω
What is the resistance of one of these bulbs?

Answer
The bulbs are identical, so they all have the same resistance.
As this is a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances.
96 Ω ÷ 8 = 12 Ω
What about parallel circuits?
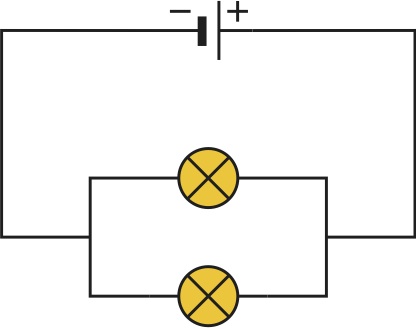
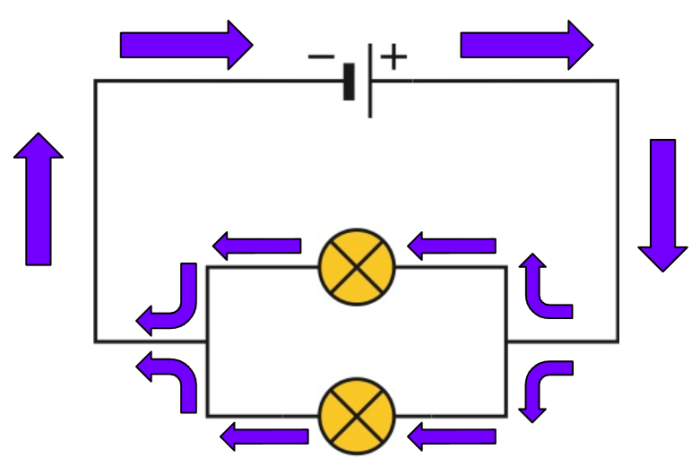
This is a parallel circuit - it has multiple pathways for the current to flow through.
Parallel circuits can have two or more 'loops' for the current to pass through. So how does the resistance of the overall circuit depend on each loop?
Here, we can visualise the current flowing through the circuit. There is a 'junction' where the current can flow one of two different ways.
Because there are multiple pathways for the current to flow, this means the resistance is lower.
In fact, in a parallel circuit, adding loops decreases the total resistance in the circuit and this means a higher current can flow!
That's quite tricky, so why not read it again before starting the questions?