Did you know that plants make carbohydrates?

When we think of carbohydrates we tend to think of food like bread and potatoes.These type of foods are called complex carbohydrates and are also known as starch.
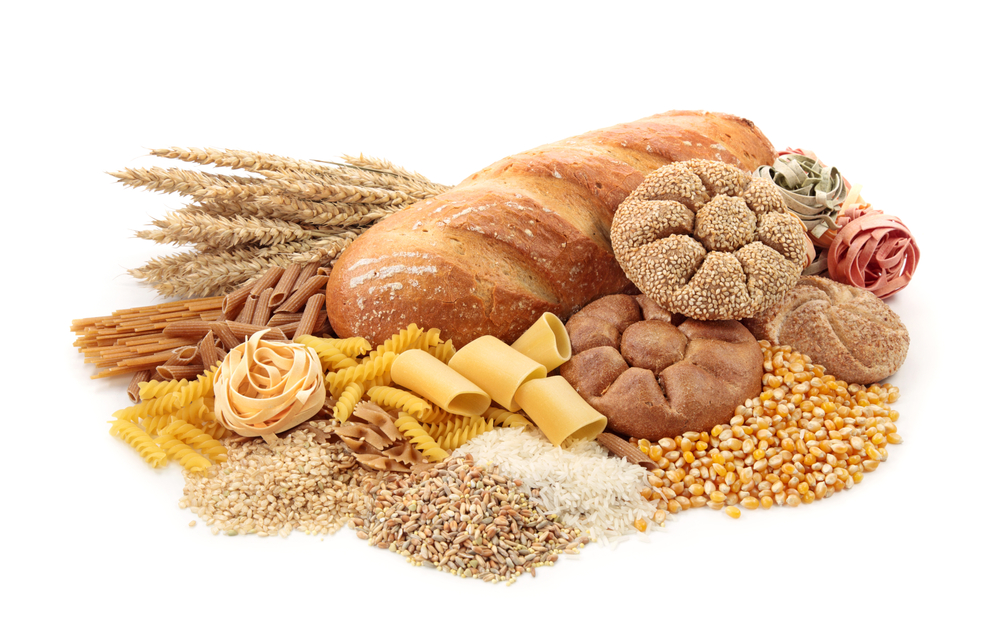

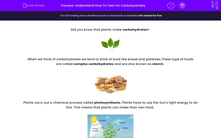
Plants carry out a chemical process called photosynthesis. Plants have to use the Sun's light energy to do this. This means that plants can make their own food.
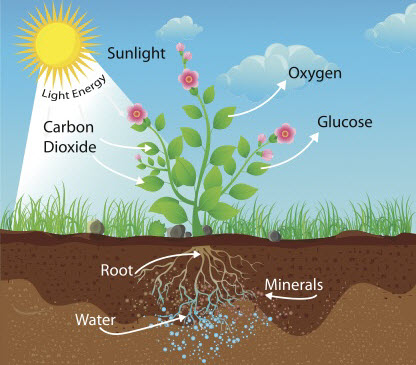
To make photosynthesis happen plants need the gas carbon dioxide and they need water. These are the reactants because photosynthesis is a chemical reaction. The carbon dioxide gas is absorbed by the plant through its leaves. The underside of a leaf has small holes called stomata - you can imagine it like an open door that allows the carbon dioxide to enter.
The water is absorbed by the plant's roots. The roots are made up of tiny cells called root hair cells which are very thin and made of only one cell. This helps the plant to absorb water really quickly through a process called osmosis. Dissolved nutrients or minerals (like nitrates, phosphates, potassium and magnesium) in the soil can be absorbed by the plant roots too.
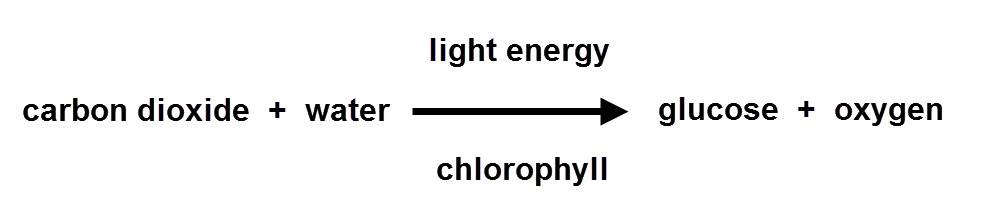
The Sun's light energy is trapped by a green pigment called chlorophyll which is found in structures called chloroplasts. The energy is used to help to convert the carbon dioxide and water into the products, glucose and oxygen. Glucose is a sugar also known as a simple carbohydrate.
We can summarise this reaction as a word equation:
So what does the plant do with the glucose?
The glucose produced in photosynthesis has a variety of uses. Some of the glucose is used to create other chemicals needed in the plant such as proteins. Some is used for respiration (when energy is released by cells) while some glucose is changed into starch and stored in the plant's leaf, stem or roots for later use. Lots of glucose joined together in a chain makes a polymer of glucose, starch:
.png)
This starch is useful because it can also be broken back down into glucose if the plant needs it for respiration. Think of a beaded necklace that has been cut - all the beads are now free!
To find evidence of carbohydrates in plants we can carry out some tests.
The iodine test is a test for starch:
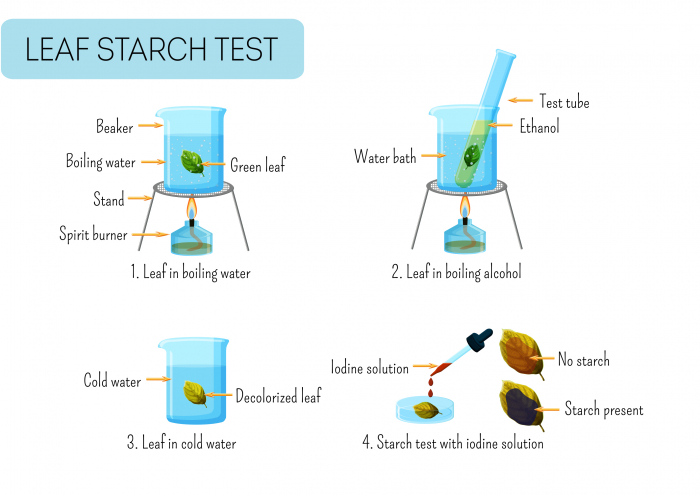
Step 1: Boil the part of the plant you want to test (for example the leaf) in water for around 10 minutes to soften.
Step 2: Place the leaf in a boiling tube containing ethanol and heat for a further 10 minutes to remove the chlorophyll from the leaf. This makes a colour change easier to see.
Important: Make sure the Bunsen/spirit burner is switched off before using the ethanol as it is highly flammable.
Step 3: Rinse the leaf with cold water.
Step 4: Add a few drops of iodine to the leaf. If the plant has any starch present (which is the carbohydrate), the iodine will turn from orange-brown to blue/black.

Another test for a carbohydrate, glucose, is called the Benedict's test.
Here, we use a blue coloured solution called Benedict's reagent/solution (named after a scientist called Stanley Rossiter Benedict).
Step 1: Place part of the plant you want to test in a pestle and mortar and add a little water to it - grind it up
Step 2: Transfer it to a boiling tube and add 1 cm3 of water
Step 3: Add 1 cm3 of Benedict's solution to the boiling tube
Step 4: Heat up the boiling tube to 95ºC in a water bath for about 5 minutes
Step 5: Record the colour of the solution
If the blue colour remains then no glucose is present. If it turns orange/brick red then glucose is present.
.jpg)
In this activity, we will look at how to test for the carbohydrates that plants make.
Let's go!